The Fourth Industrial Revolution is reshaping manufacturing and service sectors worldwide, and Thailand is at the heart of this transformation. As the nation moves towards its “Thailand 4.0” economic model, automation has become a central pillar for progress. This shift involves integrating smart technologies into production lines and business operations to enhance efficiency, productivity, and global competitiveness.
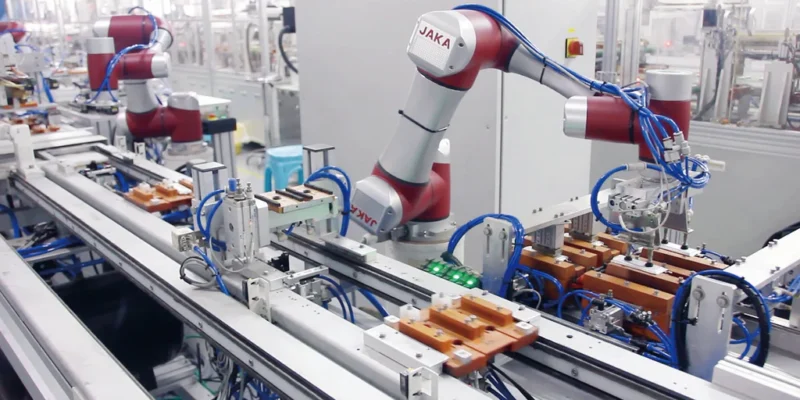
For many Thai businesses, this evolution means adopting advanced systems that streamline complex processes. The implementation of industrial automation solutions is particularly visible in the automotive, electronics, and food processing sectors. These technologies range from robotic arms on assembly lines to sophisticated software that manages supply chains. The goal is to create smarter factories and more resilient business frameworks capable of adapting to a fast-changing global market.
By integrating automation, Thai industries are not just improving their output; they are fundamentally changing their operational models. This includes using data analytics to predict maintenance needs, employing robotics for precision tasks, and using automated systems to ensure quality control. This strategic adoption helps businesses reduce human error, lower operational costs, and accelerate production cycles, positioning them for sustained growth.
The Impact on Thailand’s Workforce
The rise of automation naturally brings questions about its effect on employment. Rather than causing widespread job losses, the trend in Thailand points towards a shift in skill requirements. Repetitive and physically demanding tasks are increasingly being handled by machines. This allows human workers to focus on roles that require complex problem-solving, creativity, and strategic oversight.
Educational institutions and government bodies are responding by promoting upskilling and reskilling programmes. The focus is on developing a workforce proficient in areas like data science, robotics engineering, and systems maintenance. These initiatives aim to equip Thai workers with the necessary skills to work alongside automated systems, turning a potential challenge into an opportunity for professional development and higher-value work.
Key Sectors Leading the Charge
Thailand’s Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) is a major hub for this technological advancement. Industries within this zone are actively adopting automation to stay ahead.
- Automotive and Electronics: Robotics are used for welding, painting, and assembling intricate components with high precision. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) transport materials across factory floors, optimising logistics.
- Food and Agriculture: Smart farming techniques, including drones for crop monitoring and automated irrigation systems, are improving yields. In food processing plants, robots handle packaging and sorting, ensuring high standards of hygiene and efficiency.
This widespread adoption shows a clear commitment to building a future where technology and human ingenuity work together. Automation is helping to create a more robust, innovative, and competitive industrial base for the next generation in Thailand.








Comments